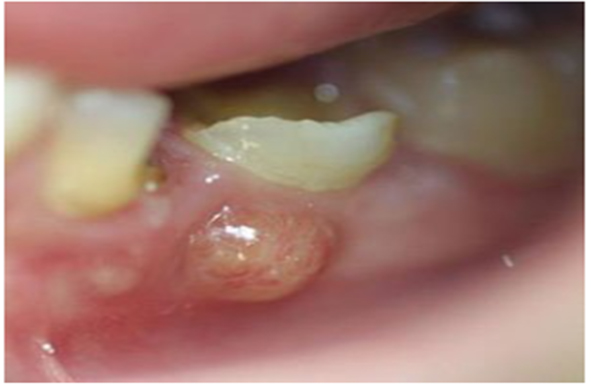
Dental Abscess:
A tooth abscess is a collection of infected material (pus) due to a bacterial infection in the center of a tooth.
Overview
- Alternate Names
- Causes
- Symptoms
- Exams and Tests
- Treatment
- Outlook(Prognosis)
- Possible Complications
- When to Contact a Medical Professional
- Prevention
Alternative Names
Periapical abscess; Dental abscess; Tooth infection; Abscessed tooth, tooth abscess, pus in the gums/mouth.
Causes
A tooth abscess is a complication of tooth decay. It may also result from trauma to the tooth, such as when a tooth is broken or chipped. Openings in the tooth enamel allow bacteria to infect the centre of the tooth (the pulp). Infection may spread out from the root of the tooth and to the bones supporting the tooth.
Infection results in a collection of pus (dead tissue, live and dead bacteria, white blood cells) and swelling of the tissues within the tooth. This causes a painful toothache. If the pulp of the tooth dies, the toothache may stop, unless an abscess develops. This is especially true if the infection remains active and continues to spread and destroy tissue.
Symptoms
The main symptom is a severe toothache. The pain is continuous and may be described as gnawing, sharp, shooting, or throbbing.
Other symptoms may include:
- Bitter taste in the mouth
- Breath odour
- General discomfort,
- uneasiness or ill feeling
- Fever
- Pain when chewing
- Sensitivity of the teeth to hot or cold
- Swelling of the gum over the infected tooth, that may look like a pimple
- Swollen Glands of the neck
- Swollen area of the upper or lower jaw — a very serious symptom
Exams and Tests
The dentist will closely look at your teeth, mouth, and gums. You may have pain when the dentist taps the tooth. Biting or closing the mouth tightly also increases the pain. The gums may be swollen and red and may drain thick material.
Dental x-rays and other tests can help your dentist determine which tooth or teeth is causing the problem.
Treatment
1.The goals of treatment are to cure the infection, save the tooth, and prevent complications.
2.Antibiotics may be given to fight the infection. Warm salt-water rinses may be soothing. Over-the-counter pain relievers may relieve the toothache and fever.
3.Do NOT place aspirin directly over the tooth or gums, because this increases irritation of the tissues and can result in Mouth ulcers.
4.A root canal may be recommended in an attempt to save the tooth.
5.If there is a severe infection, the tooth may be removed or surgery may be needed to drain the abscess. Some people may need to be admitted to the hospital.
Outlook (Prognosis)
1.Untreated abscesses may get worse and can lead to life-threatening complications.
2.Prompt treatment usually cures the infection. The tooth can usually be saved in many cases.
Possible Complications
- Loss of the tooth
- Blood infection (sepsis)
- Spread of infection to soft tissue (facial cellulitis, Ludwig’s angina)
- Spread of infection to the jaw bone (osteomyelitis of the jaw)
- Spread of infection to other areas of the body resulting in brain abscess,
- endocarditis,
- pneumonia, or other complications
When to Contact a Medical Professional?
Call your dentist if you have a persistent, throbbing toothache.
Prevention
Prompt treatment of dental caries reduces the risk of tooth abscess. Traumatized teeth should be examined promptly by the dentist.
Pus in Mouth
How to ease the pain caused by a dental abscess?
Suffering from a dental abscess can be incredibly painful and distressing. The throbbing agony, swelling, and general discomfort can disrupt your life. There are several dental procedures that can help you ease the pain and address the underlying issue.
Dental Abscess Drainage
One of the most direct methods to relieve the pain associated with a dental abscess is to drain it. During this procedure, a dentist creates a small incision in the abscess to release the accumulated pus. This process provides immediate pain relief and helps prevent the infection from spreading. It is a precise procedure performed under sterile conditions.
Root Canal Therapy
If the dental abscess is related to an infection within the tooth, a root canal procedure may be recommended. During a root canal, the infected pulp is removed, and the tooth is thoroughly cleaned, disinfected, and sealed. This not only eliminates the pain but also preserves the tooth’s structural integrity, preventing the need for extraction.
Antibiotics
In some cases, antibiotics are prescribed to control the infection associated with a dental abscess. These medications are used in conjunction with other dental procedures to address the root cause of the issue, ensuring a comprehensive treatment approach.
Tooth Extraction
In severe cases where the tooth is extensively damaged and cannot be saved, tooth extraction may be necessary. This procedure is performed with precision to minimize discomfort during and after the extraction. Afterward, replacement options, such as dental implants or bridges, can be discussed to restore your smile.
Pain Management
Effective pain management is a crucial aspect of dental abscess treatment. Dentists often use local anesthesia during procedures to minimize discomfort. Post-procedure pain relief measures are also discussed to ensure a smooth and comfortable recovery.
Preventative Care
Once your dental abscess has been treated, it’s important to maintain proper oral hygiene and attend regular check-ups to prevent future dental abscesses and other oral health issues.
If you’re suffering from a dental abscess, it’s essential to seek professional dental care to address the problem promptly. At Smileoracles Multispeciality Dental Clinic, we have the expertise and cutting-edge techniques to alleviate your pain through a range of dental procedures. Contact us today to schedule an appointment and take the first step toward relief and a healthier smile. Your well-being is our top priority.
FAQ’S
Q. Is a dental abscess contagious?
No, a dental abscess is not contagious. It is caused by bacterial infection within the tooth.
Q. How long does treatment for a dental abscess typically take?
The length of treatment for a dental abscess can vary depending on the severity of the infection and the chosen method of treatment. Antibiotics are typically taken for 5-14 days, while a root canal or tooth extraction may require multiple visits.
Q. What can I expect after treatment for a dental abscess?
After treatment, you may experience some swelling or discomfort. However, prescription pain relief medication can help manage swelling and discomfort.
Q. Will I need to take time off work or school for treatment of a dental abscess?
The need for time off work or school will depend on the severity of the infection and the chosen treatment. After a root canal or tooth extraction, it may be necessary to take a day or two off for recovery.
Q. Can I prevent dental abscess from occurring?
Maintaining good oral hygiene habits such as brushing twice a day, flossing daily, and visiting your dentist regularly can help prevent dental abscess.